Spot on Skin Itches Then Scabs Over Then Does It Again
Dermatitis is inflammation of the upper layers of the skin, causing itching, blisters, redness, swelling, and often oozing, scabbing, and scaling.
-
Known causes include dry peel, contact with a particular substance, certain drugs, and varicose veins.
-
Typical symptoms include a crimson itchy rash, scaling, open sores, oozing, and crusting.
-
The diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and confirmed by results of skin tests or skin samples or the presence of suspected drugs or irritants.
-
Avoiding known irritants and allergens (substances that crusade an allergic reaction) reduces the run a risk of dermatitis.
-
Treatment depends on the cause and the specific symptoms.
Some types of dermatitis affect but specific parts of the body (such as contact dermatitis Contact Dermatitis Contact dermatitis is skin inflammation acquired by direct contact with a item substance. The rash may be itchy, is confined to a specific area, and ofttimes has clearly defined boundaries... read more  , including poison ivy Toxicant Ivy Poison ivy is an allergic contact dermatitis that causes a very itchy rash caused by exposure to the oil urushiol, which coats the leaves of poisonous substance ivy plants. An itchy, red rash and multiple... read more
, including poison ivy Toxicant Ivy Poison ivy is an allergic contact dermatitis that causes a very itchy rash caused by exposure to the oil urushiol, which coats the leaves of poisonous substance ivy plants. An itchy, red rash and multiple... read more 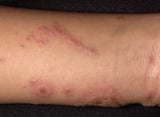 ; nummular dermatitis Nummular Dermatitis Nummular dermatitis is a persistent, normally itchy rash and inflammation of the peel characterized by coin-shaped spots and calibration. (See as well Overview of Dermatitis.) The crusade of nummular dermatitis... read more than
; nummular dermatitis Nummular Dermatitis Nummular dermatitis is a persistent, normally itchy rash and inflammation of the peel characterized by coin-shaped spots and calibration. (See as well Overview of Dermatitis.) The crusade of nummular dermatitis... read more than 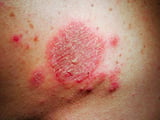 ; stasis dermatitis Stasis Dermatitis Stasis dermatitis is inflammation of the pare of the lower legs resulting from the pooling of claret and fluid. (See also Overview of Dermatitis.) Stasis dermatitis occurs in people who have... read more
; stasis dermatitis Stasis Dermatitis Stasis dermatitis is inflammation of the pare of the lower legs resulting from the pooling of claret and fluid. (See also Overview of Dermatitis.) Stasis dermatitis occurs in people who have... read more  ; lichen simplex chronicus Lichen Simplex Chronicus Lichen simplex chronicus is chronic, itchy inflammation of the top layer of the skin caused by repeated scratching, rubbing, or both. Lichen simplex chronicus involves a cycle in which scratching... read more
; lichen simplex chronicus Lichen Simplex Chronicus Lichen simplex chronicus is chronic, itchy inflammation of the top layer of the skin caused by repeated scratching, rubbing, or both. Lichen simplex chronicus involves a cycle in which scratching... read more 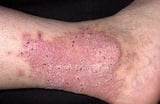 ; seborrheic dermatitis Seborrheic Dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis is chronic inflammation that causes yellowish, greasy scales and dandruff to course on areas of the peel that accept a high number of oil glands such as the scalp and face up, forth... read more
; seborrheic dermatitis Seborrheic Dermatitis Seborrheic dermatitis is chronic inflammation that causes yellowish, greasy scales and dandruff to course on areas of the peel that accept a high number of oil glands such as the scalp and face up, forth... read more 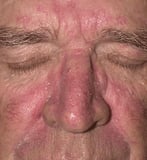 ; and manus and foot dermatitis Mitt and Foot Dermatitis Hand and human foot dermatitis is a chronic dermatitis characterized by cherry, scaly, thickened pare on the hands, the feet, or both. (See also Overview of Dermatitis.) Hand and foot dermatitis oftentimes... read more than
; and manus and foot dermatitis Mitt and Foot Dermatitis Hand and human foot dermatitis is a chronic dermatitis characterized by cherry, scaly, thickened pare on the hands, the feet, or both. (See also Overview of Dermatitis.) Hand and foot dermatitis oftentimes... read more than 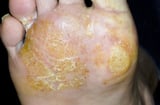 ), whereas others can occur anywhere (such as atopic dermatitis Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) Atopic dermatitis (ordinarily referred to as eczema) is chronic, itchy inflammation of the upper layers of the skin that often develops in people who have hay fever or asthma and in people who... read more
), whereas others can occur anywhere (such as atopic dermatitis Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema) Atopic dermatitis (ordinarily referred to as eczema) is chronic, itchy inflammation of the upper layers of the skin that often develops in people who have hay fever or asthma and in people who... read more 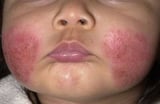 ).
).
Chronic dermatitis persists over a long period of time. The hands are peculiarly vulnerable to chronic dermatitis, because the hands are in frequent contact with many strange substances. Chronic dermatitis can have many different causes. Chronic scratching and rubbing because of itching often results in thickening of the pare (lichenification).
Dermatitis causes
-
Redness
-
Itching
-
Scaling
-
Swelling
-
Oozing
-
Crusting
-
Blisters (sometimes)
-
Thickening of peel, or lichenification (in chronic dermatitis)
Chronic dermatitis often results in thickening of skin and cracks in the peel. Whatever blazon of dermatitis may exist complicated past an infection.
-
A doctor's examination
-
Pare or blood tests or both
-
Sometimes biopsy
Doctors base the diagnosis of dermatitis on the person'south symptoms and on what the rash looks like and where information technology appears on the body. Doctors attempt to determine whether the person has come in contact with an irritating substance, has an allergy, or has an infection.
-
Avoidance of triggers
To reduce the risk of dermatitis, people should avoid known allergens and irritating substances (triggers).
-
Supportive care (such as moisturizers and dressings, and antihistamines for itching)
-
Topical corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive (drugs that decrease the immune organization responses) creams or ointments
-
Sometimes antibiotics
-
Sometimes systemic (bodywide) immunosuppressive drugs or injections
-
Sometimes ultraviolet (UV) light therapy
CLICK HERE FOR THE PROFESSIONAL VERSION

© 2022 Merck Abrupt & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA
Source: https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/skin-disorders/itching-and-dermatitis/overview-of-dermatitis
Post a Comment for "Spot on Skin Itches Then Scabs Over Then Does It Again"